The Julian calendar, introduced by Julius Caesar in 45 BCE, was based on a 365-day year with an extra day added every four years to account for the extra 0.25 days in a solar year. This additional day was inserted at the end of February, creating a leap year. However, over time, this system caused the calendar to drift out of sync with the solar year.
In the Julian calendar, a year is 365.25 days long, which is slightly longer than the actual solar year of 365.2425 days. This discrepancy led to inaccuracies in the calendar, with the equinoxes and solstices occurring earlier each year. By the 16th century, the Julian calendar was approximately 10 days behind the solar year.
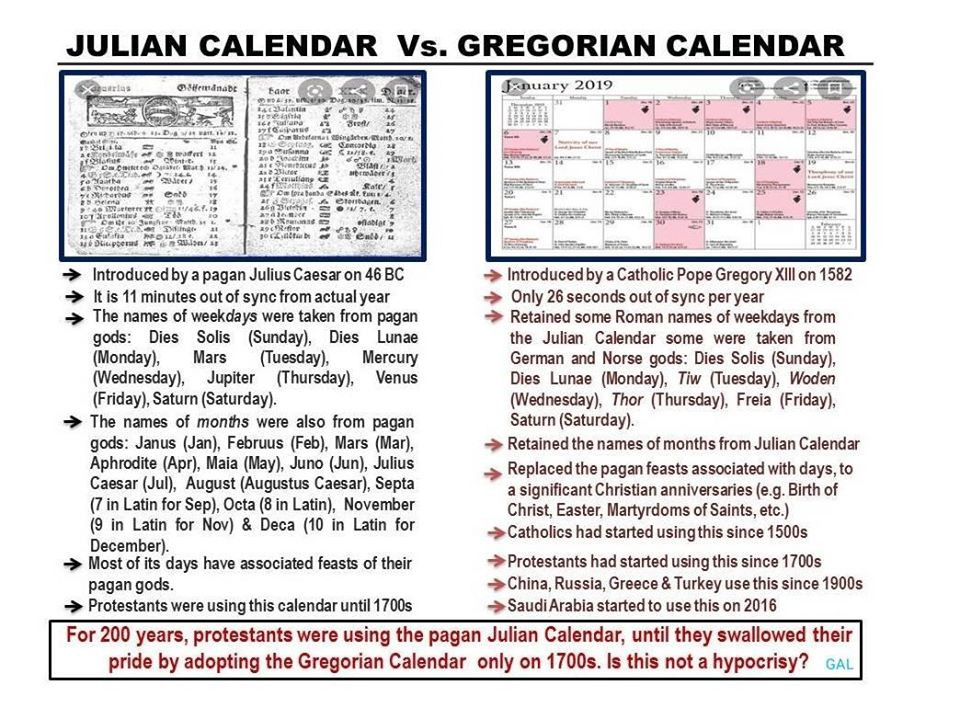
Julian Vs Gregorian Calendar Difference
The Gregorian Calendar
To address the inaccuracies of the Julian calendar, Pope Gregory XIII introduced the Gregorian calendar in 1582. The key difference between the Julian and Gregorian calendars is the leap year rule. In the Gregorian calendar, a year is considered a leap year if it is divisible by 4, except for years that are divisible by 100 but not by 400.
The Gregorian calendar also made a one-time adjustment by skipping 10 days to bring the calendar back in line with the solar year. This adjustment was made in October 1582, with the day after October 4th being declared October 15th. The Gregorian calendar is now the most widely used calendar system in the world.
Key Differences
In summary, the Julian calendar used a leap year rule based on adding a day every four years, while the Gregorian calendar refined this rule to account for the slight discrepancy in the solar year. The Gregorian calendar also made a one-time adjustment to align the calendar with the solar year, which the Julian calendar did not do.
Overall, the Gregorian calendar is a more accurate and reliable calendar system compared to the Julian calendar, which had significant inaccuracies due to its leap year rule. The Gregorian calendar is now used by most countries around the world for civil purposes and is the standard calendar for international business and communication.