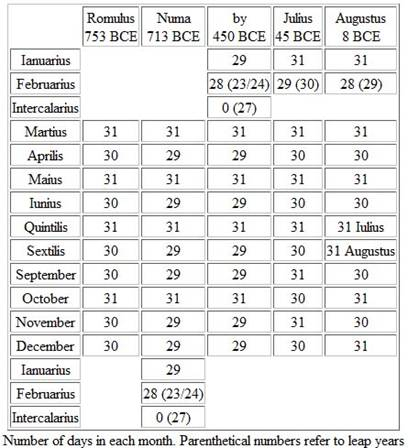
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the ancient Romans and is believed to have been created by Romulus, the legendary founder of Rome, around 753 BC. It was a lunar calendar consisting of 10 months, with the year starting in March. The Roman calendar had only 304 days, and to account for the remaining days in a solar year, an additional month called Mercedonius was added every two years.
Over time, the Roman calendar fell out of sync with the seasons, causing confusion and chaos. In 46 BC, Julius Caesar introduced the Julian calendar to reform the outdated system and align it with the solar year.
Roman Calendar Vs Julian Calendar
Julian Calendar
The Julian calendar, introduced by Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar and is the precursor to the Gregorian calendar we use today. The Julian calendar consisted of 12 months and 365 days, with a leap year occurring every four years to account for the extra quarter of a day in the solar year.
While the Julian calendar was a significant improvement over the Roman calendar, it still had flaws due to the slight miscalculation of the length of the solar year. This led to the eventual adoption of the Gregorian calendar in 1582 to further refine the system and correct the inaccuracies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Roman calendar and Julian calendar are two historical calendars that played a crucial role in shaping the way we measure time. While the Roman calendar laid the foundation for timekeeping in ancient Rome, the Julian calendar represented a significant advancement in calendar reform. Both calendars have influenced the development of modern calendars and continue to be studied for their historical significance.